Content Index
How can we move this character from point A to point B in Unreal Engine?
This is useful when we have an enemy or similar and we want it to automatically move between points A and B.
For this, we use a pair of vectors, A being global:
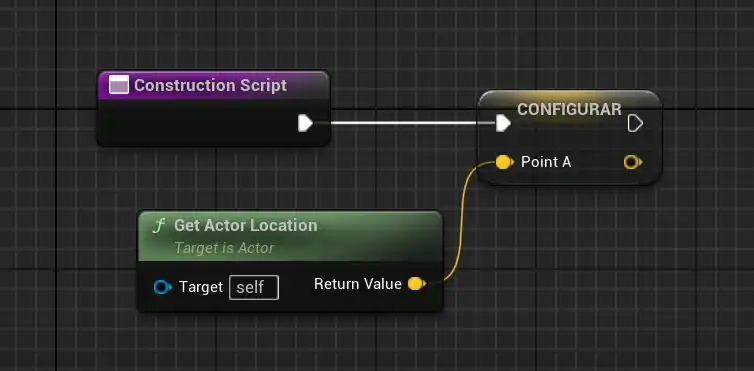
And B, which is relative and in which we activate the widget to be able to view and move it:
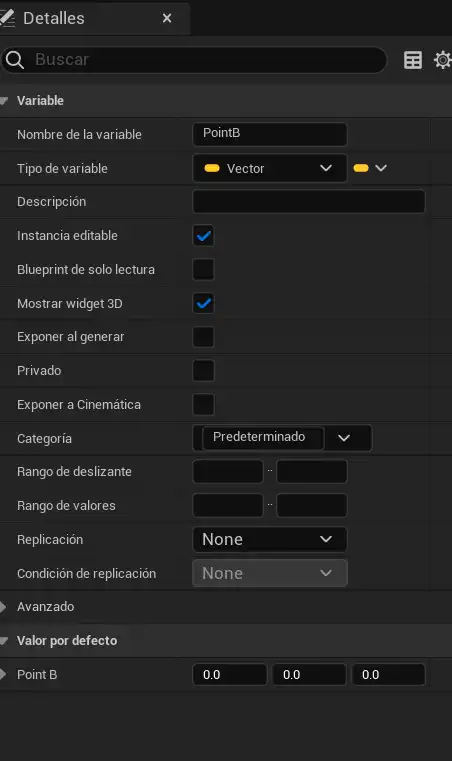
Now, how do we make it move from point A to point B? It's very simple. This isn't really the main part I want to explain, but I'll mention it anyway.
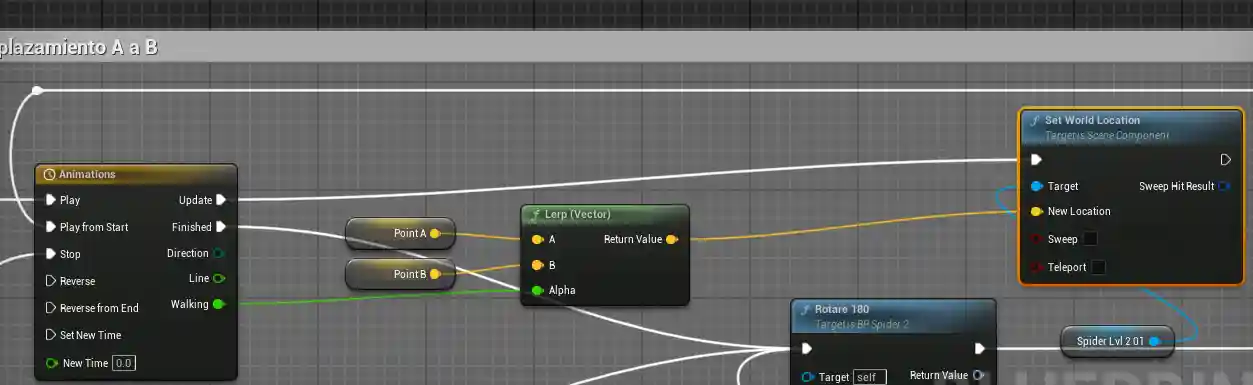
The Timeline and Interpolation
Here we have the timeline. As always, there are many ways to do it, but this is the most traditional:
Global and Relative Positions
I initialize position A in the constructor, obtaining the character's global position. So far, so good, since A will always be the return point.
The problem arises with position B, which is dynamic and relative.
If B is at 0,0,0, it is equivalent to position A.
From there, it moves, but it remains relative.
A global position would be that of an object in the world (e.g., a spider).
A relative position depends on another (e.g., the moon relative to the Earth), and in this example, the Earth would have a global position in the universe.
So if I move B to (300,0,0), that is not a global position, but relative to A. To make it global I would have to add the coordinates of A and B.
The Problem of Rotations
So far it seems simple, but the real dilemma arises with rotations.
If I just added A and B, it would work fine for positions, but not for rotations.
I tried several solutions. One of them was:
- Get the character's rotation.
- Multiply that rotation by B.
- Then add the position of A.
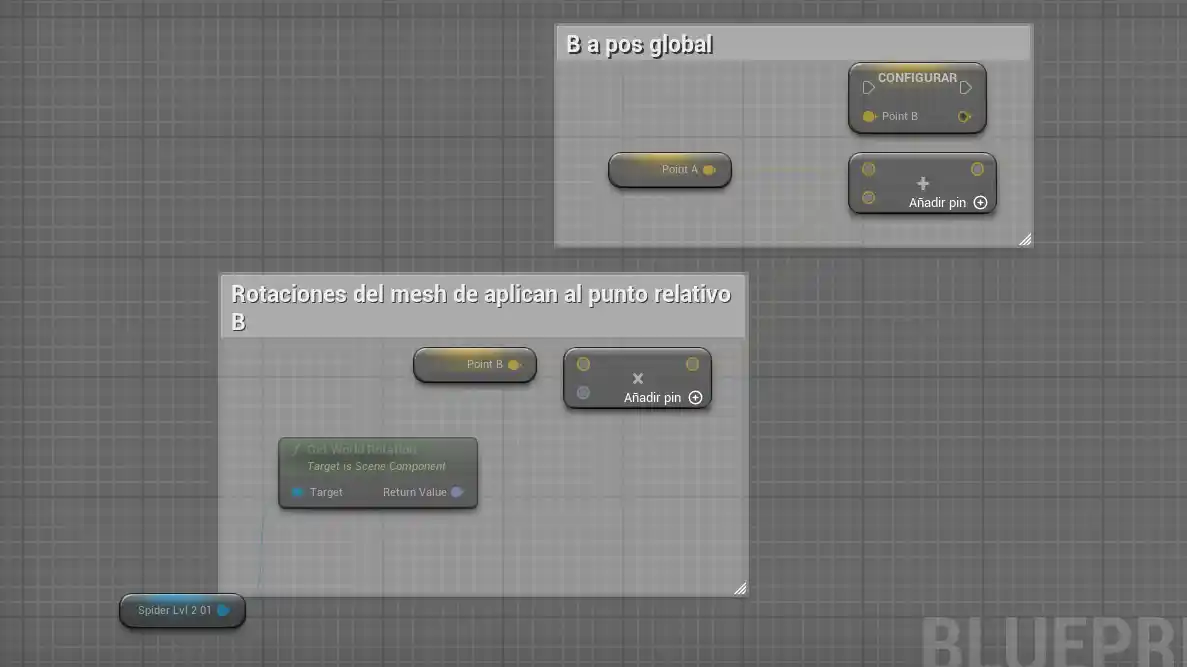
This worked to a certain extent, but when applying more complex rotations, the results broke down.
The Right Solution: Transform Location
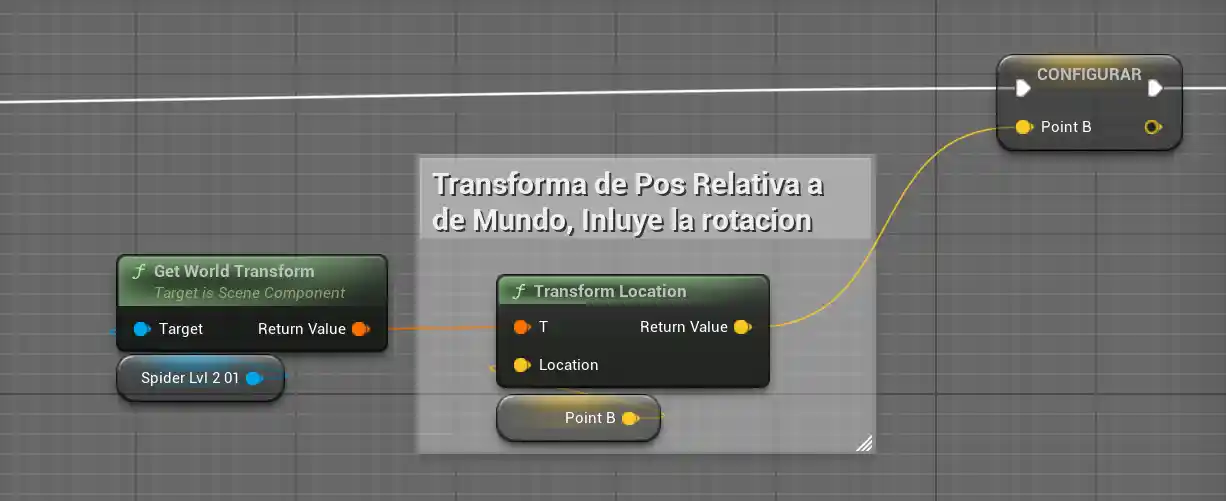
I finally discovered a node that solves this problem: Transform Location.
This node transforms a local location into a global location.
The flow is simple:
- I get the A (global) position.
- I use the GetWorldTransform node to access the scale, translation, and rotation.
- I pass B (relative) through the Transform Location node.
- Voilà, B is now converted to global coordinates.
- With this, any rotation works correctly and the movement remains stable.
Conclusion
If you want to move an object from local to global positions, the most practical approach is to use the Transform Location node.
This way, you can work with interpolations, relative movements, and rotations without breaking the system.
