When you work with Flask and need to connect your backend with another app (for example, a frontend in Vue or React), sooner or later you'll encounter the dreaded CORS error, at this point, we already have our Rest API created in Flask, now we want to be able to connect to it from other apps.
In my case, it happened when consuming a Flask API from a Vue app: the browser blocked the requests for security reasons.
The solution lies in understanding what CORS is, how to configure it correctly in Flask, and, above all, how to do it securely.
What is CORS and why is it necessary in Flask?
CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing) is a mechanism that allows one domain to access resources from another domain.
By default, browsers block requests between different origins for security reasons.
This means that if you have your Flask API running on localhost:5000 and your Vue frontend on localhost:8080, the requests will be blocked... unless you enable CORS.
In my experience, this "makes perfect sense": in 99% of cases, we don't want other domains modifying our data.
But in this interconnected world — with mobile, web apps, and microservices — we need to open that door in a controlled and secure way.
That's where Flask-CORS comes into play.
We can define CORS as:
Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS (en-US)) is a mechanism that allows configuring a server to obtain permissions to access selected resources of said server from a different origin (domain).
And this is according to the definition we have on Mozilla:
https://developer.mozilla.org/es/docs/Web/HTTP/CORS
As an example, if we have a Flask App, we create a Rest API as we create in the full course and we want to consume it from a Vue app:
Content Index
- What is CORS and why is it necessary in Flask?
- ⚙️ Install Flask-CORS in your Python project
- Configure CORS in Flask in a controlled and secure way
- What this code does:
- CORS in development vs production
- Common errors and how to solve them
- Quick debugging tips
- ⚡ Alternatives and advanced configurations
- Conclusion and final best practices
- ❓ Frequently Asked Questions about Flask CORS (FAQs)
By default, the server will block any request coming from another domain, which makes perfect sense since in 99.99 percent of cases we will be interested in no other app or domain being able to perform operations on our app.
Although in this interconnected world, where we create a web app, but then we create other apps to improve access to it depending on the device, and therefore we create additional apps, whether mobile with Flutter, Vue Native, React, Native Android, Vue... we need to open that door to be able to communicate these apps with our personal cloud, and in these cases, we can use CORS to open this door in a controlled and secure way;
As Flask is a micro framework, we have to install a dependency or package to be able to use this feature, in this post we select the following one:
https://flask-cors.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
Remember to have your app created, a hello world in Flask, and your rest api in Flask.
⚙️ Install Flask-CORS in your Python project
Flask is a minimalist microframework, so to use CORS we must install an external package:
Which once installed:
pip install flask-corsConfigure CORS in Flask in a controlled and secure way
First, import the module and configure it on your Flask application:
We perform the typical configurations
#CORS
from flask_cors import CORS
cors = CORS(app, resources={r"/api/*": {"origins": "http://localhost:8080"}})What this code does:
- /api/* refers to which part of the domain you will allow sharing; generally, you don't need to enable access to the entire app, but only to your rest api, which generally starts with the suffix of "api" which is the one we enable.
- Don't use "*" except for local testing.
- In the origin, we can place them all with *, or a particular one; in this case, we place localhost and port 8080 which is the Vue app in development mode
with this, from our Vue app, we can consume our rest:
fetch("http://localhost:5000/api/products/")
.then((res) => res.json())
.then((res) => (this.products = res));And see the response from the browser:

Without the use of CORS in Flask:
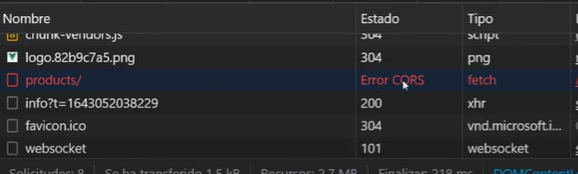
Before enabling CORS, the browser showed an error:
“Access to fetch at 'http://localhost:5000/api/products/' from origin 'http://localhost:8080' has been blocked by CORS policy.”
CORS in development vs production
During development, it's common to use origins='*' to simplify testing, but never do it in production.
In real environments, you must specify the exact domains:
CORS(app, resources={r"/api/*": {"origins": ["https://miapp.com", "https://admin.miapp.com"]}})This ensures that only your official applications can communicate with the API.
Common errors and how to solve them
Error Cause Solution
Blocked by CORS policy You did not configure Flask-CORS or the origin does not match. Verify the exact value of the origin.
No 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' header The header was not sent correctly. Review your CORS(app, ...) configuration.
Error with OPTIONS method The browser makes a “preflight request”. Enable OPTIONS methods in your API or let Flask-CORS handle it automatically.
Quick debugging tips
Check the browser console: there you will see which domain and header is blocking the request.
Use curl to test outside the browser:
curl -i -X GET http://localhost:5000/api/products/Activate verbose mode in your frontend to see sent CORS headers.
⚡ Alternatives and advanced configurations
Flask-CORS also allows using a decorator per route, ideal if you only want to enable CORS on certain endpoints:
from flask_cors import cross_origin
@app.route("/api/products")
@cross_origin(origins="http://localhost:8080")
def products():
return jsonify({"message": "ok"})This gives you more control when you have public and private routes in the same application.
You can also define configurations using environment variables, which is recommended in large projects.
Conclusion and final best practices
- Use CORS only where necessary.
- Limit the origins. Don't use * in production.
- Centralize the configuration.
- Always test with your actual frontend before publishing.
- In my case, enabling CORS correctly was key to connecting Flask with Vue and continuing to develop without browser blocks, but you can connect it with any other technology like React, Angular, Flutter…
❓ Frequently Asked Questions about Flask CORS (FAQs)
1. What is Flask-CORS and how does it work?
It is a Flask extension that automatically adds the necessary headers (Access-Control-Allow-Origin, etc.) to allow requests between domains.
2. How to test if my Flask API has CORS active?
You can make a fetch request from another domain or use curl -I to see if the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header appears.
3. Can I use Flask-CORS only on specific endpoints?
Yes, with the @cross_origin() decorator applied to the desired routes.
4. How to solve the CORS error when using fetch?
Make sure that the frontend origin is authorized in Flask-CORS and that the API responds correctly to OPTIONS requests.
Next step, learn how to implement your first unit and integration tests in Flask.
