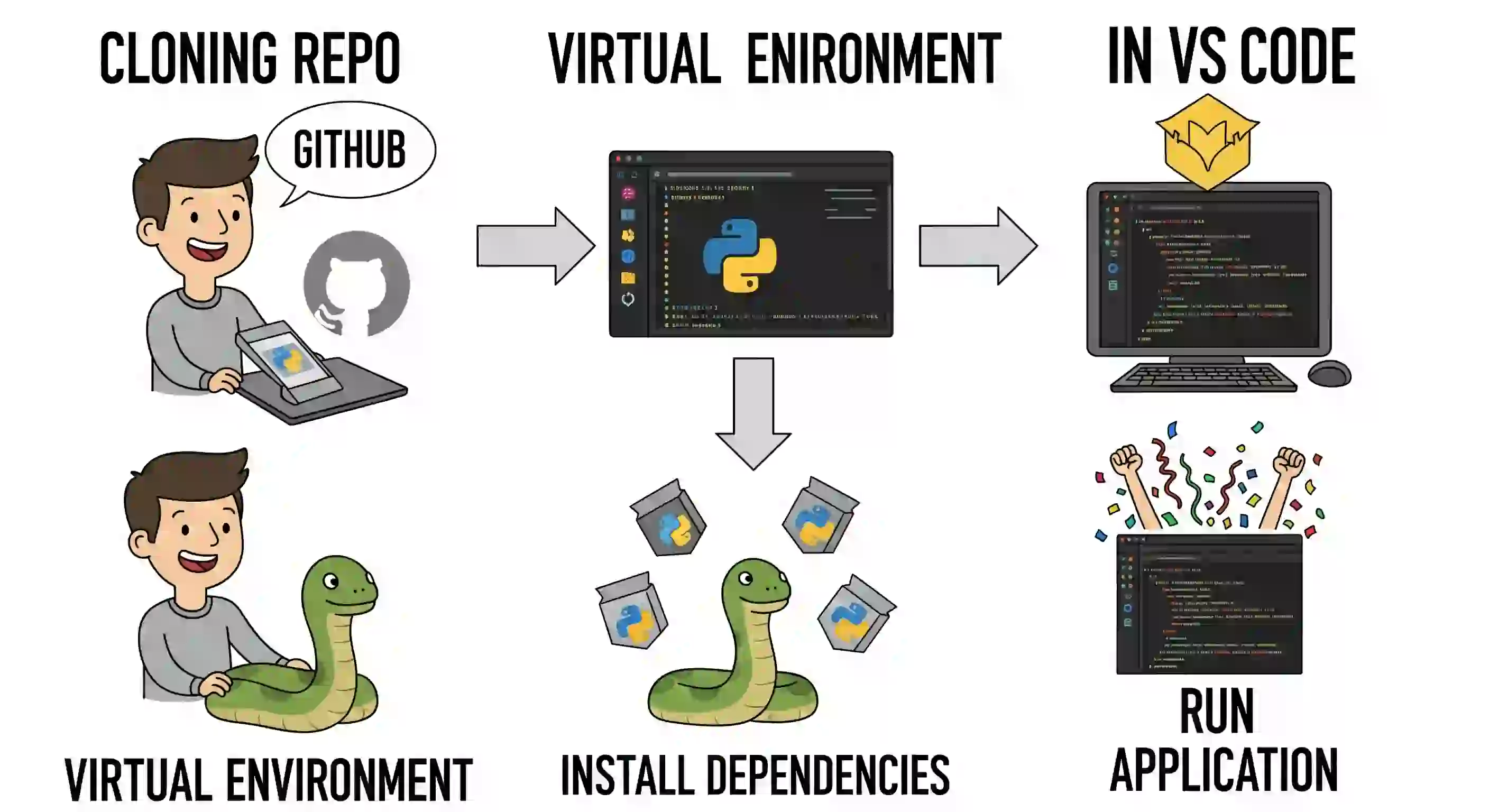
I'm going to explain how you can download a Python project from GitHub so you can develop it using a virtual environment. That is, we'll set up the environment, download the project, and install its dependencies.
Prerequisites
- First: this is a private project, but that doesn't matter. The steps are the same whether it's public or private.
- Second: I'm assuming you already have Git configured in your terminal. I won't explain it here; I'm focusing only on the steps for cloning the project and setting up the virtual environment.
Check your Python version
A little extra detail: I had an older version of Python on my Mac and had to record this video twice. When I tried to install the specific versions required by the project, it told me they couldn't be installed because Python was outdated.
The project requires Django 5, so you'll need to make sure you have a compatible version of Python.
If you don't know how to update it, here's a video that explains how.
Installing minimal global dependencies
In this example, I'm going to use venv. As you can see, by updating Python, I no longer have any globally installed packages. In my case, I have to use pip3 to install packages, although pip would normally suffice. That depends on your operating system... it's a God's errand.
So, I install virtualenv with:
$ pip3 install virtualenvThis will be the only package we'll install globally for the operating system. Everything else must be installed within the project's virtual environment.
You can verify that it's installed with:
$ pip3 freezeAnd you will see that only virtualenv appears.
Prepare the project folder
Now, we'll close this terminal and make sure we have an empty folder where we'll work. In my case, the folder is called courses. The virtual environment and then the cloned project will be placed there.
If you manage multiple projects, I recommend creating one folder per project. In my case, I'll do everything here.
Create the virtual environment from VS Code
Open a new instance of VS Code. To avoid conflicts, I recommend creating the environment from VS Code, as it better recognizes packages and enables auto-completion.
Also, make sure you have the Microsoft Python extension installed.
Then press:
Ctrl+Shift+P (o Cmd+Shift+P en Mac)Find and select Python: Create Environment.
Select your project folder (in my case, Courses) and then the Python version you want to use (use the new one, not the old one).
VS Code will create the environment in that folder. If the environment name appears in parentheses in the terminal, it was activated successfully. If not, you may need to activate it manually.
A surefire way to verify you're in the virtual environment is to run:
$ pip3 freezeAnd check that only what's installed in that environment (e.g., virtualenv) appears. If more appears, you're probably using the global environment.
Clone the project from GitHub
Now, let's clone the repository. Remember, you already have Git configured. Open the terminal and run:
$ git clone https://github.com/usuario/repositorio.gitRename the folder if you want (in my case I renamed it to django-shopping).
Install project dependencies
Once the project is cloned, navigate inside its folder:
$ cd django-shoppingAnd then install the dependencies using the requirements.txt file:
$ pip3 install -r requirements.txtThis will install exactly the versions needed for the project.
Check once again with pip3 freeze to make sure the dependencies are now active. If necessary, you can also check that they are not installed in the global environment.
Conclusion
And that's it! You now have your virtual environment up and running with all the project dependencies, cloned from GitHub.
So, these are the steps you need to follow to successfully work with Python projects, a virtual environment, and a repository from GitHub.