When I started working with DataTable in Flutter, the first thing I discovered is that this widget is ideal for displaying tabular information in an organized and visually clear way. It is the classic table with rows and columns, but adapted to the Material ecosystem.
Remember that we want to create a side menu in Flutter.
1. What is DataTable in Flutter and what is it for
A DataTable is a user interface component used to display data in a table format. It is typically used in web or mobile applications to present data in an interactive grid with rows and columns. Users can interact with a DataTable to sort, search, filter, and paginate large volumes of data, which makes it a useful tool for presenting information clearly and easily accessible. In short, a DataTable is a user interface element used to display data in an interactive table.
A Flutter DataTable allows:
- Sorting columns
- Highlighting rows
- Adding edit icons
- Integrating text, images, buttons, and any widget
- Displaying simple or complex tables
Although it works great as a static table, it is not always responsive by default on mobile, especially when the table has multiple columns. Therefore, it is key to understand how to combine it with other widgets to get the best experience.
2. How to create your first DataTable (practical example)
We are going to introduce a very useful Flutter widget, which is DataTable, to present data in an organized way in a Flutter grid or table; to present information, and this information can be text, images, buttons—which are widgets in short; let's present all the code for the example we are going to analyze:
DataTable(
sortColumnIndex: 2,
sortAscending: false,
columns: [
DataColumn(label: Text("Nombre")),
DataColumn(label: Text("Apellido")),
DataColumn(label: Text("Años"), numeric: true),
],
rows: [
DataRow(
selected: true,
cells: [
DataCell(Text("Andrés"), showEditIcon: true),
DataCell(Text("Cruz")),
DataCell(Text("28")),
],
),
DataRow(
cells: [
DataCell(Text("Ramos")),
DataCell(Text("Ayu")),
DataCell(Text("999")),
],
),
],
)With this, we achieve a simple table like the following:
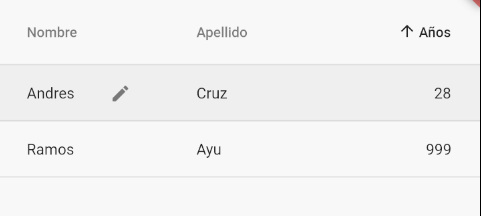
As you may know if you are also a web developer or have also tried to use grids on mobile platforms, grids are not adaptive, which makes data visualization complicated; but with this widget, we can use it in conjunction with others that will even allow us to create horizontal scrolling, etc.
When I tried it for the first time, I noticed two things:
- showEditIcon only draws the icon, it doesn't make the cell editable (I thought it edited too).
- Setting selected: true highlights the row with a soft gray, useful for visual feedback.
Configure a DataTable in Flutter
The table or Datatable in its minimal configuration needs to define the `DataColumn` to define the column labels and the `DataRow` which are for defining the data within the `rows` property (in addition to the `DataTable` itself, of course); what you have to keep in mind is that you must define the same number of `DataColumn` as `DataCell` within a `DataRow`.
There are multiple properties you can use as you like to customize the columns, rows, cells, or the table itself; let's look at some of the main ones:
Selected Row
Through `selected` in the `DataRow`, you can indicate that you want to highlight a specific row, which will appear with a soft gray, just like you can see in the image above.
Editable Cell
Through `showEditIcon` in the `DataCell`, you can specify a pencil icon to indicate that the cell in question can be editable, although this does not mean that this attribute implements editing in the cell; all it does is draw that icon.
Sorting
We can also set representative icons to show that a column can be sorted; for that, we can indicate the index of the column you want to sort with `sortColumnIndex` and indicate whether you want to show the icon to sort ascendingly or not with `sortAscending`.
3. Essential Properties of the DataTable Widget
- DataColumn
- Here you define the columns. The important thing is to maintain coherence: if you have 3 DataColumn, your DataRow must have 3 DataCell.
- DataRow
- Each row of the table. Something I learned through experimenting is that you can highlight a row using selected: true to give context to the user.
- DataCell
- Each cell in the row. Here you can place almost any widget.
The attribute showEditIcon: true shows the pencil, but does not implement editing (you have to do that yourself).
- Each cell in the row. Here you can place almost any widget.
- Sorting (sort)
- When I was configuring sorting, I had to play with:
- sortColumnIndex
- sortAscending
- When I was configuring sorting, I had to play with:
This allows Flutter to display the sort icon in the header and apply your sorting logic.
4. How to make a DataTable responsive in Flutter
One of the first obstacles I had was that DataTables don't adapt well by default on mobile, especially when there are many columns.
Here are the most practical solutions:
Horizontal Scroll
The simplest and most effective:
SingleChildScrollView(
scrollDirection: Axis.horizontal,
child: DataTable(...),
)This is one way to prevent columns from being cut off on small screens.
Column Adjustment
You can wrap the content in FittedBox, or adjust the Text with softWrap and overflow. It depends on the level of density you want in your table.
Best Practices
- Avoid more than 5 columns on mobile
- Use abbreviations when necessary
- Always test in landscape and portrait
- You are in Flutter, everything is reactive, detect the screen size and adapt the number of rows
5. Optimization: how to handle tables with a lot of data
The DataTable is not efficient for thousands of rows, because it renders everything at once.
Here are some considerations:
- Pagination
- Start dividing the rows into pages so that Flutter doesn't have to render everything.
- Using PaginatedDataTable
- A more professional alternative, ideal for large datasets:
- Includes pagination by default
- Takes up less memory
- Is more UX-friendly
- Implementation with DataTableSource
- If you need superior performance, use a DataTableSource-based model, which allows you to:
- Load only visible rows
- Connect with APIs
- Implement lazy-loading
- Performance tips
- Disable functions you don't use (sort, selection)
- Avoid heavy widgets inside DataCell
- Use const whenever you can
6. Advanced Examples and Real-World Cases
One of the things that surprised me most when I started using DataTable is how flexible it can be:
- Tables with images (avatars)
- Cells with action buttons
- Tables connected to streams
- Tables with horizontal + vertical scroll
- Tables with custom filters
In my case, I once needed to display a table with 10 columns; the only viable way was to wrap it in a horizontal SingleChildScrollView and control the size of each column manually.
⭐ 1. DataTable with horizontal and vertical scroll
Ideal when you have many columns and many rows.
SizedBox(
height: 400,
child: SingleChildScrollView(
scrollDirection: Axis.vertical,
child: SingleChildScrollView(
scrollDirection: Axis.horizontal,
child: DataTable(
columns: const [
DataColumn(label: Text("ID")),
DataColumn(label: Text("Nombre")),
DataColumn(label: Text("Correo")),
DataColumn(label: Text("Rol")),
DataColumn(label: Text("Estado")),
],
rows: List.generate(20, (index) {
return DataRow(
cells: [
DataCell(Text("$index")),
DataCell(Text("Usuario $index")),
DataCell(Text("user$index@mail.com")),
DataCell(Text(index % 2 == 0 ? "Admin" : "User")),
DataCell(Text(index % 2 == 0 ? "Activo" : "Inactivo")),
],
);
}),
),
),
),
)⭐ 2. DataTable with actions inside DataCell
Buttons, icons, and useful actions.
DataTable(
columns: const [
DataColumn(label: Text("Producto")),
DataColumn(label: Text("Precio")),
DataColumn(label: Text("Acciones")),
],
rows: [
DataRow(cells: [
DataCell(Text("Laptop")),
DataCell(Text("\$1200")),
DataCell(
Row(
children: [
IconButton(
icon: Icon(Icons.edit),
onPressed: () {
print("Editar");
},
),
IconButton(
icon: Icon(Icons.delete, color: Colors.red),
onPressed: () {
print("Eliminar");
},
),
],
),
)
])
],
)⭐ 3. Editable DataTable (with dialog)
A simple but elegant flow.
void _editarCelda(BuildContext context, String valorInicial) async {
TextEditingController controller = TextEditingController(text: valorInicial);
await showDialog(
context: context,
builder: (_) => AlertDialog(
title: Text("Editar valor"),
content: TextField(
controller: controller,
),
actions: [
TextButton(
onPressed: () => Navigator.pop(context),
child: Text("Cancelar"),
),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: () {
print("Nuevo valor: ${controller.text}");
Navigator.pop(context);
},
child: Text("Guardar"),
),
],
),
);
}
DataTable(
columns: const [
DataColumn(label: Text("Nombre")),
DataColumn(label: Text("Edad")),
],
rows: [
DataRow(
cells: [
DataCell(
Text("Andrés"),
showEditIcon: true,
onTap: () => _editarCelda(context, "Andrés"),
),
DataCell(
Text("28"),
showEditIcon: true,
onTap: () => _editarCelda(context, "28"),
),
],
),
],
)⭐ 4. Dynamically generated DataTable from a list
Very common when loading data from an API or database.
final List<Map<String, dynamic>> usuarios = [
{"nombre": "Luis", "edad": 21, "pais": "México"},
{"nombre": "Laura", "edad": 32, "pais": "Perú"},
{"nombre": "Akira", "edad": 29, "pais": "Japón"},
];
DataTable(
columns: const [
DataColumn(label: Text("Nombre")),
DataColumn(label: Text("Edad")),
DataColumn(label: Text("País")),
],
rows: usuarios
.map(
(u) => DataRow(
cells: [
DataCell(Text(u["nombre"])),
DataCell(Text(u["edad"].toString())),
DataCell(Text(u["pais"])),
],
),
)
.toList(),
)⭐ 5. Full PaginatedDataTable (ideal for many rows)
class UsuariosDataSource extends DataTableSource {
final List<Map<String, dynamic>> usuarios;
UsuariosDataSource(this.usuarios);
@override
DataRow? getRow(int index) {
if (index >= usuarios.length) return null;
final user = usuarios[index];
return DataRow(
cells: [
DataCell(Text(user["id"].toString())),
DataCell(Text(user["nombre"])),
DataCell(Text(user["email"])),
],
);
}
@override
bool get isRowCountApproximate => false;
@override
int get rowCount => usuarios.length;
@override
int get selectedRowCount => 0;
}Usage:
PaginatedDataTable(
header: Text("Usuarios"),
columns: const [
DataColumn(label: Text("ID")),
DataColumn(label: Text("Nombre")),
DataColumn(label: Text("Email")),
],
source: UsuariosDataSource([
{"id": 1, "nombre": "Ana", "email": "ana@mail.com"},
{"id": 2, "nombre": "Carlos", "email": "carlos@mail.com"},
{"id": 3, "nombre": "Mina", "email": "mina@mail.com"},
]),
rowsPerPage: 2,
)⭐ 6. DataTable with custom formatting (colors and styles)
DataTable(
headingRowColor: MaterialStateProperty.all(Colors.blueGrey),
headingTextStyle: TextStyle(color: Colors.white, fontWeight: FontWeight.bold),
dataRowColor: MaterialStateProperty.resolveWith<Color?>(
(states) {
if (states.contains(MaterialState.selected)) {
return Colors.blue.withOpacity(0.2);
}
return null;
},
),
columns: const [
DataColumn(label: Text("Tarea")),
DataColumn(label: Text("Estado")),
],
rows: [
DataRow(
selected: true,
cells: [
DataCell(Text("Revisar PR #32")),
DataCell(Text("En progreso")),
],
),
DataRow(cells: [
DataCell(Text("Actualizar documentación")),
DataCell(Text("Pendiente")),
]),
],
)7. Conclusion
Creating a table in Flutter with DataTable is straightforward, but mastering it requires understanding its limits and how to extend it.
Personally, I think it is ideal for small or medium tables and for administrative interfaces. But when your dataset grows, it's convenient to migrate to
PaginatedDataTable or DataTableSource-based solutions.
With the right practices, it is an extremely useful and flexible widget.
❓ FAQs
- How do I make a DataTable editable in Flutter?
- showEditIcon only shows the icon. You must handle the onTap of the DataCell and open a dialog or form.
- Is DataTable suitable for large lists?
- To a certain extent. More than 1000 rows can be slow. For that, use PaginatedDataTable or DataTableSource.
- What is the difference between DataTable and PaginatedDataTable?
- DataTable shows all the data; PaginatedDataTable divides it into pages and improves performance.
Next step, learn how to use the GestureDetector widget to implement click events, among others, in any widget in Flutter.
